What is LM358?
The LM358 is a widely used dual operational amplifier (op-amp) integrated circuit (IC) known for its versatility, reliability, and low cost. Developed by various manufacturers like Texas Instruments, ON Semiconductor, and others, the LM358 is commonly used in a variety of analog electronic circuits due to its ease of use and broad range of applications. Here are some key points about the LM358:
- Type: Dual Operational Amplifier
- Number of Amplifiers: 2 independent op-amps in a single package
- Package: Typically available in DIP, SOIC, and other form factors
- Power Supply Voltage: Usually operates with a single power supply, accommodating a wide range of voltages
- Input Offset Voltage: Typically low, ensuring accurate amplification
- Input Bias Current: Typically low for most applications
- Key Features: Low input bias current, low offset voltage, versatile input voltage range
Main Characteristics and Uses of the LM358:
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications, including signal amplification, filtering, and comparators.
- Low Power Consumption: Ideal for battery-powered systems or low-power applications.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Known for its affordability and availability.
- Compatibility: Works well with single or dual power supply configurations.
Common Applications of the LM358 Include:
- Filter Circuits: Used in active filter designs for frequency selection.
- Signal Conditioning: Amplifying and processing signals from sensors, transducers, or other sources.
- Comparator Circuits: Employed to compare two voltage levels and activate based on certain conditions.
- Voltage Followers: Acting as buffer stages to isolate loads from input sources.
Working Principle:
- Each op-amp within the LM358 independently amplifies the voltage difference between its inputs based on its gain.
- The LM358 can be configured in various ways to perform different functions based on the application requirements.
- Proper external component selection and configuration are crucial for achieving desired amplification characteristics.
In summary, the LM358 is a versatile and commonly used dual op-amp IC that is well-suited for a wide range of analog circuit applications. Designers and hobbyists frequently rely on the LM358 for its ease of use, reliability, and cost-effectiveness when developing various electronic projects and systems.
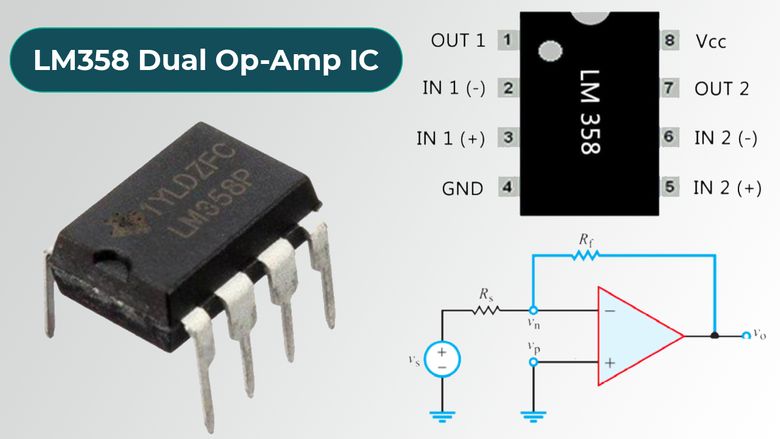
LM358 Pinout

Pin Configuration
| Pin No. | Pin Name | Description |
| 1 | Output A | This pin is the output of first operational amplifier |
| 2 | Inverting Input A | This pin is the inverting input of first op-amp |
| 3 | Non inverting Input A | This pin is the non-inverting input of first op-amp |
| 4 | Ground (GND) | This pin is the non-inverting input of first op-amp |
| 5 | Non inverting Input B | This ground or negative supply to op-amp |
| 6 | Inverting Input B | This pin is the non-inverting input of second op-amp |
| 7 | Output B | This pin is the output of the second op-amp |
| 8 | Vcc | This pin is the positive voltage supply to both op-amp |
LM358 Features & Specification
The LM358 is a dual operational amplifier IC with two independent op-amps in a single package. Here are the key features and specifications of the LM358:
Features:
- Dual Operational Amplifier: Contains two separate op-amps in a single package.
- Low Power Consumption: Suitable for battery-operated and low-power applications.
- Wide Supply Voltage Range: Typically operates from a single power supply voltage, typically ranging from 3V to 32V.
- Low Input Bias Current: Ensures minimal impact on the input signal.
- Low Offset Voltage: Provides accurate amplification with minimal input voltage variation.
- High Input Impedance: Easy to interface with various sensors and sources.
- Unity Gain Stable: Maintains stability even at unity gain (gain of 1).
- Output Short Circuit Protection: Ensures the op-amp is not damaged in case of output shorts.
- Internally Frequency Compensated: Simplifies external circuitry requirements.
- Wide Temperature Range: Typically operates over a wide temperature range for versatility.
Specifications:
- Supply Voltage: Typically operates with a single power supply voltage, commonly ranging from 3V to 32V.
- Input Offset Voltage: Typically in the range of a few millivolts.
- Input Bias Current: Typically in the range of tens of nanoamperes.
- Common Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR): Typically 70-90 dB.
- Gain Bandwidth Product: Typically a few megahertz.
- Slew Rate: Typically a few volts per microsecond.
- Operating Temperature Range: Typically varies depending on the manufacturer but often spans from -40°C to 125°C.
- Package Options: Available in various packages like DIP (Dual Inline Package), SOIC (Small Outline Integrated Circuit), and TSSOP (Thin Shrink Small Outline Package).
Applications:
- Signal Conditioning: Used in amplifiers, filters, and signal processing circuits.
- Voltage Followers: Acts as buffers to isolate and drive loads from input sources.
- Comparators: Utilized for voltage comparison and decision-making in electronic circuits.
- Active Filters: Implementing active filter designs for desired frequency response.
- Sensor Signal Processing: Interfacing with sensors to amplify and process sensor signals.
- Oscillator Circuits: Used in oscillator circuits for generating specific waveforms.
Note:
- The LM358 is widely used in various analog applications due to its simplicity, versatility, and reliability.
- Designers select the LM358 for its ease of use, wide supply voltage range, and cost-effectiveness in many electronic projects.
LM358 Circuit
LM358 Application Circuits
The LM358 is a versatile dual operational amplifier IC commonly used in a wide range of analog applications. Here are some common application circuits using the LM358:
1. Inverting Amplifier:
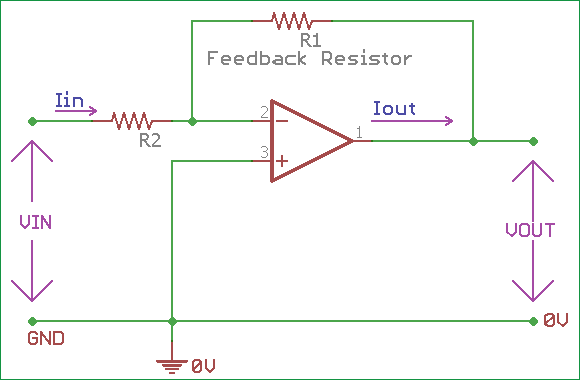
- Description: This circuit amplifies the input signal with an inverted polarity.
- Components: LM358, resistors, input signal source.
- Function: The gain of the amplifier is set by feedback resistor values.
- Equation: Output voltage = -(Rf / Rin) * Vin
- Example: Used in audio applications, where the phase of the signal does not matter.
2. Non-Inverting Amplifier:
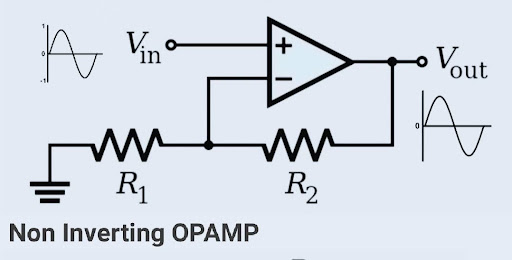
- Description: This circuit amplifies the input signal without inverting its polarity.
- Components: LM358, resistors, input signal source.
- Function: The gain is set by the resistor values in the circuit.
- Equation: Output voltage = (1 + Rf / Rin) * Vin
- Example: Widely used in signal conditioning and instrumentation applications.
3. Summing Amplifier:
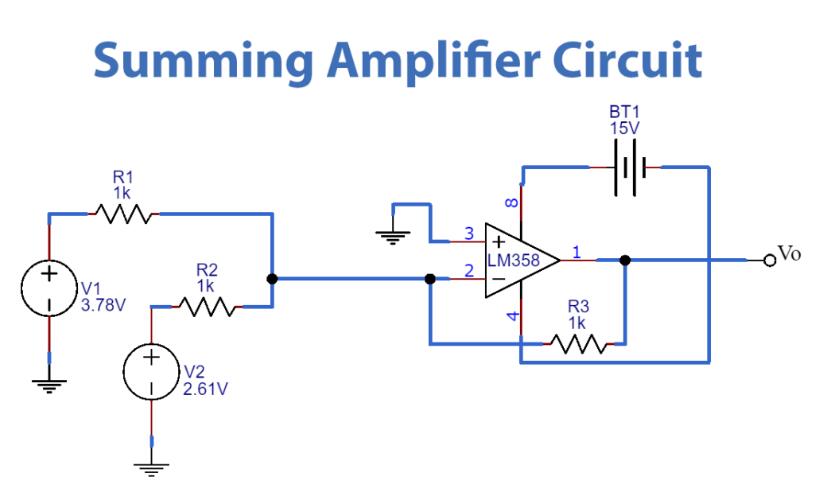
- Description: Combines multiple input signals into a single output.
- Components: LM358, resistors, input signal sources.
- Function: Each input signal's contribution to the output is determined by the resistor ratios.
- Equation: Output voltage = -Rf1*(Vin1/Rin1) - Rf2*(Vin2/Rin2) - ...
- Example: Used in signal mixing and audio applications for combining different sources.
4. Voltage Follower:
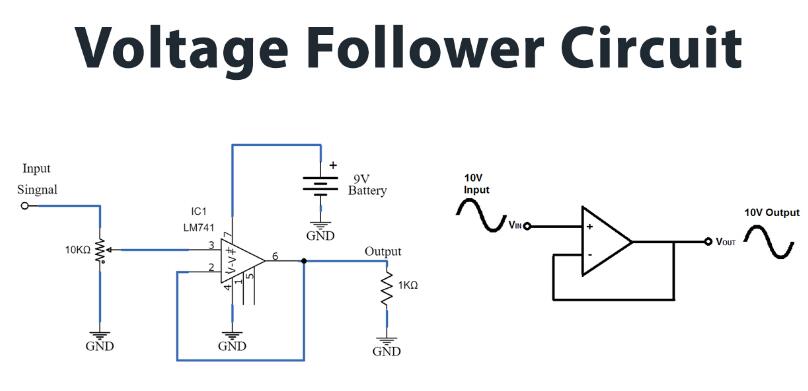
- Description: Provides high input impedance and low output impedance buffering.
- Components: LM358, input signal source, feedback resistor.
- Function: Output voltage mirrors the input voltage.
- Equation: Output voltage ≈ Input voltage
- Example: Used to prevent loading effects in sensor circuits and to drive low impedance loads.
5. Comparator Circuit:
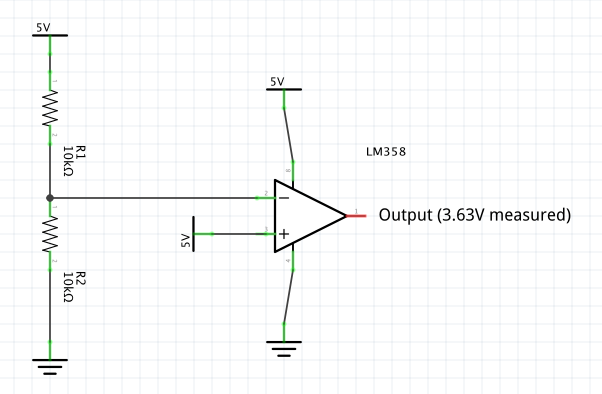
- Description: Compares two input voltages and provides a digital output.
- Components: LM358, resistors, input signal sources.
- Function: Outputs a high or low digital signal based on the differential input voltage.
- Example: Used in threshold detection, monitoring circuits, and signal level detection.
6. Active Low-Pass Filter:
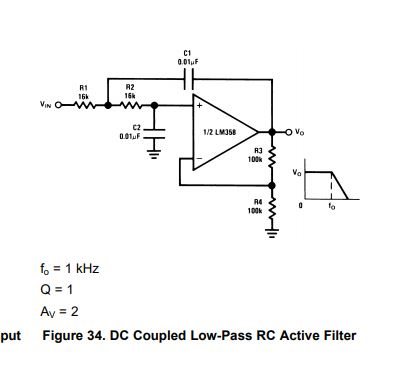
- Description: Filters out high-frequency components from the input signal.
- Components: LM358, capacitors, resistors.
- Function: Passes low-frequency signals while attenuating high frequencies.
- Example: Used in audio applications to remove noise or high-frequency interference.
These are just a few examples of the many application circuits that can be implemented using the LM358 dual operational amplifier IC. Each circuit design serves a specific purpose, such as amplification, filtering, mixing, or comparison, showcasing the versatility of the LM358 in various analog electronic systems. When designing circuits, always refer to the LM358 datasheet and consider the specific requirements of your application.
LM358 Operating Principle & Working
LM358 Operating Principle & Working:
Overview:
The LM358 is a dual-operational amplifier (op-amp) IC that contains two independent op-amps in a single package. These op-amps are designed to amplify voltage differences between their two input terminals and produce an output voltage based on this difference. Here is an overview of the operating principle and working of the LM358:
Basic Op-Amp Structure:
- An op-amp consists of differential input terminals labeled as the non-inverting input (+) and the inverting input (-).
- It has a high input impedance, a high gain, and a low output impedance.
Internal Circuitry:
- The LM358 features internal circuitry that includes differential input stages, gain stages, and output stages for each op-amp.
- Each op-amp has a well-defined gain-bandwidth product that limits the frequency at which high gain can be maintained.
Operating Principle:
- Input Stage: The LM358's input stage compares the voltage difference between the non-inverting and inverting inputs.
- Amplification Stage: The op-amp amplifies this voltage difference based on its defined gain.
- Output Stage: The amplified output signal is provided at the op-amp output pin.
Working:
-
Power Supply Connection:
- The LM358 is typically powered by a dual or single power supply depending on the application.
- Proper power supply connections are essential for the op-amp to function correctly.
-
Input Signal Connection:
- An input signal is applied to the non-inverting or inverting input terminals of the op-amp.
- The choice of the input terminal depends on the circuit design and the desired functionality (inverting/non-inverting amplifier, comparator, etc.).
-
Feedback Configuration:
- The LM358 is often used in feedback configurations where part of the output is fed back to the inverting or non-inverting input.
- This feedback determines the overall gain and behavior of the op-amp circuit.
-
Output Signal:
- The amplified output signal is available at the op-amp output pin.
- The output swing of the LM358 is typically limited to the power supply rails.
-
Negative Feedback Mechanism:
- Negative feedback is commonly employed to stabilize the op-amp and set its gain.
- It helps in reducing distortion and improving the linearity of the amplifier.
-
Output Range Adjustment:
- The output of the LM358 can be adjusted using external components like resistors to set the gain of the amplifier according to the application requirements.
-
Applications:
- The LM358 is widely used in various applications such as amplifiers, filters, sensor interfaces, and comparators due to its reliable performance and ease of use.
LM358 Advantages
The LM358 operational amplifier is a popular choice in various analog circuit designs due to its numerous advantages. Here are some of the key advantages of using the LM358 IC:
1. Versatility:
- The LM358 is a dual operational amplifier, which means it contains two op-amps in a single package, offering flexibility in designing circuits that require multiple amplifiers.
2. Cost-Effective:
- It is a cost-effective solution for basic operational amplifier requirements, making it popular in applications where cost is a significant factor.
3. Ease of Use:
- The LM358 is relatively straightforward to use, especially for beginners and hobbyists due to its simple configuration and minimal external components required for basic operations.
4. Wide Operating Voltage Range:
- The LM358 can operate over a wide range of voltages (typically from a single 3V to 32V supply), making it suitable for a variety of applications.
5. Low Power Consumption:
- It has low power consumption, making it suitable for battery-operated devices and other low-power applications.
6. High Input Impedance:
- The LM358 has a high input impedance, making it compatible with a wide range of input sources and reducing loading effects on the input signal.
7. Unity Gain Stable:
- The LM358 is stable even at unity gain (gain of 1), making it suitable for applications where unity gain is required.
8. Robustness:
- The LM358 is a robust IC that can handle a wide range of temperatures and environmental conditions, ensuring reliability in various operating conditions.
9. Single or Dual Supply Operation:
- The LM358 can operate on both single and dual power supplies, adding to its versatility in circuit design.
10. Proven Performance:
- With a long history in the industry, the LM358 has been extensively used in various applications, demonstrating its proven performance and reliability.
LM358 Equivalents
The LM358 series is equivalent to one-half of the LM324. ICs with matching characteristics can be regarded as equivalents of the LM358. These include LM158, LM258, LM2904, and LM2409. Although these ICs may have slight differences in thermal properties, they are generally suitable replacements for most projects.
For potential replacements, consider: GL 358, NE 532, OP 04, OP 221, OP 290, OP 295, OPA 2237, TA7 5358-P, UPC 358C, AN 6561, CA 358E, and HA 17904.
LM358 Datasheet
Download LM358 Datasheet PDF from Onsemi or Texas Instruments.
LM358 IC Packages
The LM358 Dual Op-Amp IC is available in four distinct package types: DSBGA, PDIP, TO-CAN, and SOT-25(5). For detailed information regarding these packages, including their dimensions and part numbers, please refer to the tabular diagram provided below.
| LM 358 IC Packages | ||
| Package | Dimension | Unit |
| DSBGA(8) | 1.31 X1.31 | mm |
| PDIP(8) | 1.91 X6.35 | mm |
| T0-CAN(8) | 9.08 X 9.31 | mm |
| S0IC(8) | 4.90 X 3.91 | mm |

FAQ
- What is LM358 used for?
-
LM358 finds versatile applications as a transducer amplifier, a DC gain block, and more. It boasts a substantial DC voltage gain of 100dB. This integrated circuit (IC) offers flexibility by operating within a broad power supply range, from 3V to 32V for single power supply setups and from ±1.5V to ±16V for dual power supply configurations. Additionally, it supports a wide output voltage swing.
- What is the difference between LM741 and LM358?
-
LM358 functions as a low-power operational amplifier, while IC 741 serves as a voltage comparator.
- Can LM324 and LM358 be replaced?
-
The LM358 is an 8-pin dual operational amplifier, whereas the LM324 is a 14-pin quad operational amplifier. Both share identical parameters, which allows for interchangeability, albeit requiring some adjustments to the circuit board. If employed as a comparator within an inverter, this substitution poses no issues. In my opinion, the LM358 is a preferable choice, given its simpler circuit board design. However, when the operational amplifier serves as an oscillator, I recommend replacing it with high-speed op amps such as the TL082 and TL084.
- Can use LM358 and LM358s interchangeably in circuit?
-
While both can serve similar purposes, LM358S offers improved performance. If precision and speed are crucial, it's recommended to use LM358S.
- What are the advantages of LM258 compared to LM358?
-
The LM258 is categorized as an industrial-grade component, while the LM358 falls under the commercial-grade classification. Notably, the LM258 holds a higher grade status compared to the LM358, boasting superior parameters. Among these chips, the LM258 stands out as a high-performance option.



